Watershed Assessment Tool for Environmental Risk (WATER)
Overview
WATER model is designed to evaluate the risk associated with different sediment control measures. The modeling approach of the risk assessment model is conceptually similar to that of the Water Erosion Prediction Project model (Flanagan and Nearing. 1995). With WATER model, a climate generator WINDS is used to simulate many years of weather realization that utilized to estimate corresponding soil erosion.
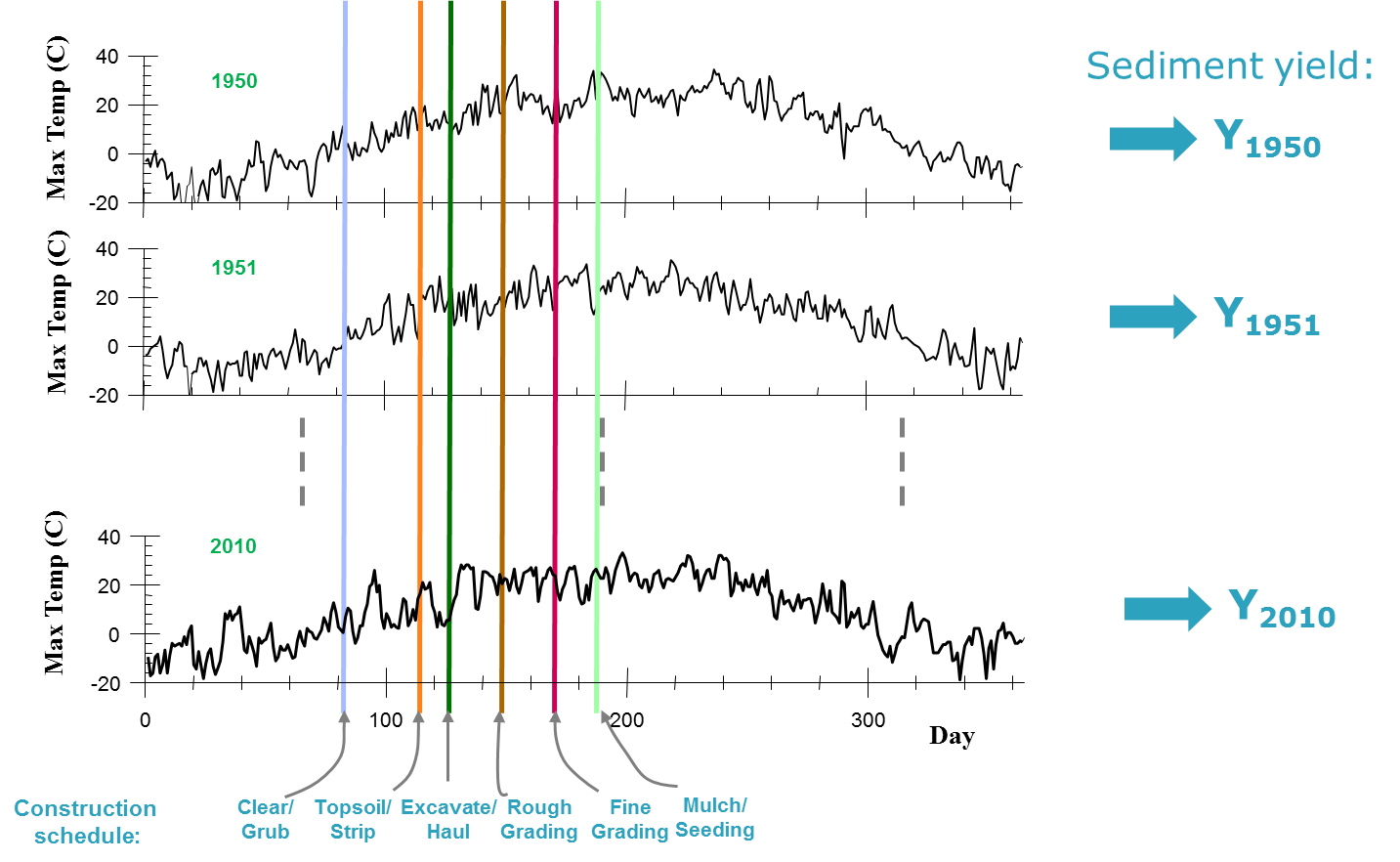
Framework
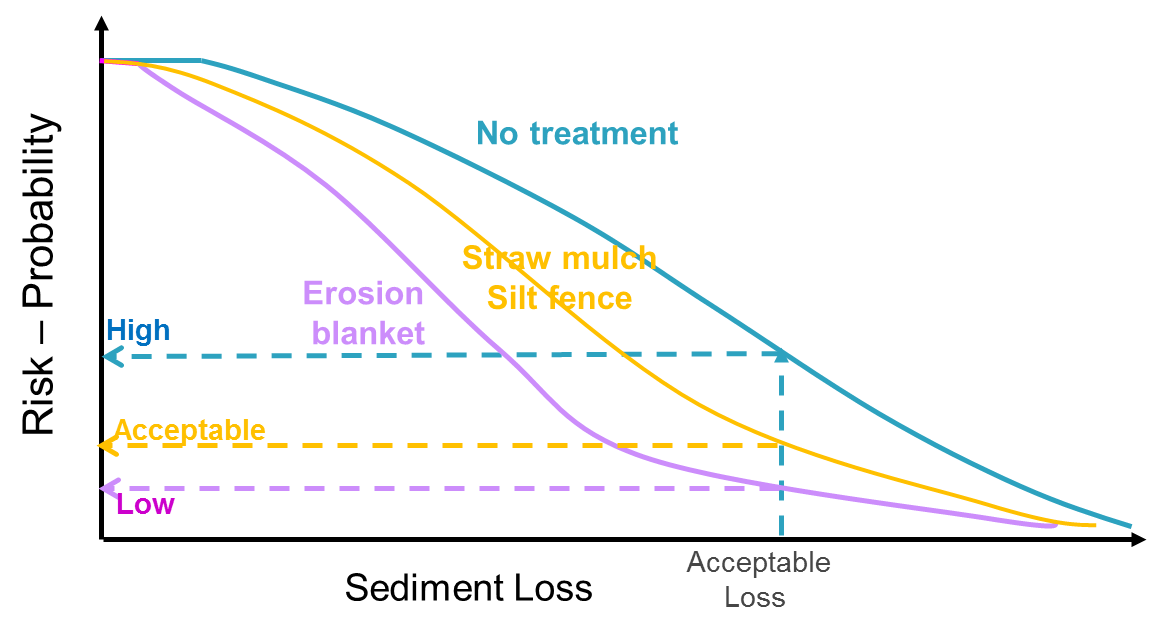
Risk assessment of erosion on constuction site is done in the WATER model by simulating plant growth, runoff, and erosion at the site after the start of construction activities. These processes depend on weather condition and simulations exhibit different responses for each weather realization during a construction. Total sediment yield is obtained by summing the sediment yield for individual storms occurring after site disturbance. This process is repeated for different sediment control practices for each year of generated weather conditions. For a large number of weather realizations, probabilistic analyses of sediment yield data are possible. If the user has an acceptable sediment loss goal, then the fraction of years that have yields less than or equal to the goal can be determined for each of the scenarios.
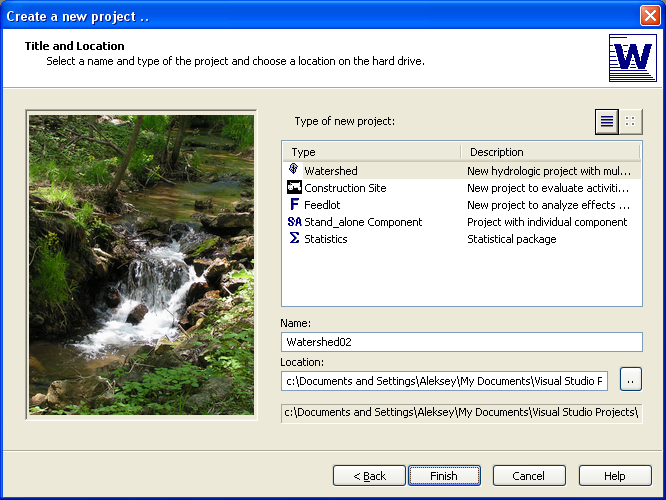
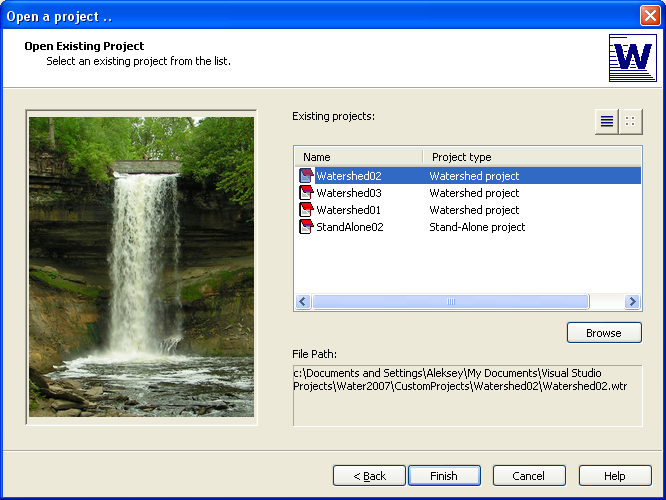
Graphical User Interface
WATER graphical user interface was developed with Visual Studio C++ and MapWindow GIS ActiveX control. Object-oriented programming allowed each model component to be individually wrapped as a class for better model integration. GIS viewer was developed to help with GIS geospatial input data files.
Relevant publications:
- Wilson, B.N., A.Y. Sheshukov, and R. Pulley (2006) Erosion risk assessment tool for construction sites, Minnesota Department of Transportation, Report MN/RC-2006-27, 72 p.
- Wilson, B., and A.Y. Sheshukov (2006) A process based erosion and sediment model for construction sites. ASCE Conf. Proc. 200, 415. DOI:10.1061/40856(200)415.
- Wilson, B.N., A.Y. Sheshukov, and A. Mendez (2008) Design Tool for Controlling Runoff and Sediment from Highway Construction, Minnesota Department of Transportation, Report MN/RC-2008-35, 109 p.
- Wilson, B.N, A.Y. Sheshukov and A. Mendez (2009) Simulation of Rock Infiltration Systems, Proceedings of the 2009 ASABE Annual International Meeting, ASABE Paper No. 096995, Reno, NV.
